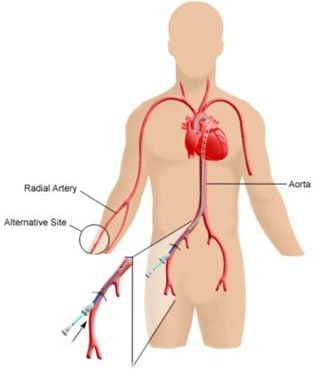
A coronary angiogram is a procedure that uses X-ray to see your heart's blood vessels using contrast media (Dye). The test is generally done to see if there is any blockage to the blood flow going to the heart.
Your doctor may recommend that you have a coronary angiogram if you have:
First Distal Radial Angiography at Apollo New Delhi
Snaring to Remove Broken Catheter (Avoided Surgery)
It is performed with the use of local anesthesia and intravenous sedation, it is performed either through the leg or through the hand . We perform most of the cases through the hand as patient can move just after the procedure unlike if it is done through the leg.
In performing a coronary angiogram, a doctor inserts a small catheter through the skin into an artery in either the groin or the arm. The catheter is then advanced to the opening of the coronary arteries (the blood vessels supplying blood to the heart). Next, a small amount of radiographic contrast is injected into each coronary artery. The images that are produced are called the angiogram. The procedure takes approximately 30 minutes.
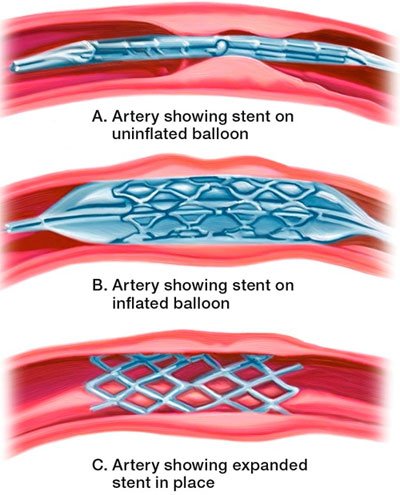
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA), is a minimally invasive, endovascular procedure to widen narrowed or blocked arteries. Successful angioplasty also means you might not have to undergo a surgical procedure called coronary artery bypass surgery. This surgery requires an incision in the chest, and recovery from bypass surgery is usually longer and more uncomfortable.
General anesthesia isn’t needed. You’ll be awake during the procedure. You’ll receive fluids, medications to relax you and blood-thinning medications through an IV catheter.
Angioplasty is performed by a heart specialist (cardiologist) and a team of specialized cardiovascular nurses and technicians in a special operating room called a cardiac cath lab.
First Distal Radial Angioplasty at Apollo New Delhi
Bilateral Renal Angioplasty
Using Proglide to Close Puncture to Avoid Surgery
Most people who have angioplasty also have a stent placed in their blocked artery during the same procedure. The stent is usually inserted in the artery after it’s widened by the inflated balloon.
If you had a non emergency procedure, you’ll probably remain hospitalized one day while your heart is monitored and your medications are adjusted. You generally should be able to return to work or your normal routine the week after angioplasty. If you needed angioplasty and stenting during a heart attack, your hospital stay and recovery period will likely be longer. It’s important that you closely follow your doctor’s recommendations about your treatment with blood-thinning medications — aspirin and clopidogrel or similar medications.
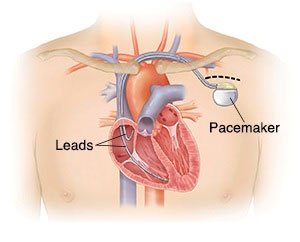
A pacemaker is an electronic device that prevents your heart from becoming too slow.
Pacemaker is generally implanted when your heart rate becomes too slow , this results in low blood pressure and you start to feel dizziness and may even lose consciousness.
Pacemaker is implanted through one of chest veins. The area is anesthetized and through a needle a wire is inserted through which all procedure is done. Patient remains conscious and generally he is discharged in a day or two.
ICD stands for implantable cardioverter defibrillator. It is an advanced pacemaker device that corrects the heart rhythm by delivering electrical impulses.
As a rule of thumb ICD are implanted in patients at high risk of sudden cardiac death.
Defibrillators treat arrhythmias in two ways: in the first instance the device tries to stop the abnormal rhythm with a burst of high speed pacing (cardioversion). If that fails, the device will deliver an electrical impulse to the heart to reset its rhythm (defibrillation).
No, It can usually be safely implanted under local anesthesia.
At our centre we allow patients to walk the next day and the patient goes home on day 3. Generally no restriction of activities is required after day 3.

CRT stands for cardiac resynchronization therapy. It is an advanced pacemaker device that improves the functioning of heart by altering the flow of electrical impulses in heart and by making the heart chambers to contract in synchronous mode.
CRT is done in patients with poor heart function (generally less than 40%) and having disturbed electrical conduction( what is called as bundle branch block).
The CRT device is implanted by venous approach, us¬ing fluoroscopic guidance to place pacing lead through the cephalic, axillary, or subclavian veins into the right atrium, right ventricle, and a tributary of the coronary sinus(CS).
No, It can usually be safely implanted under local anesthesia
At our centre we allow patients to walk the next day and the patient goes home on day 3. Generally no restriction of activities is required after day 3.
There are two types of CRT: CRT-P and CRT-D.
Carotid artery stenting is a procedure in which a cardiologist inserts a a stent, which expands inside your carotid artery to increase blood flow in areas where blood flow is obstructed.
As a rule of thumb carotid stenting is done when one or more of carotid arteries are blocked by more than 70%. Carotid Arteries are blood vessels that supply blood to brain , obstruction in one of the vessels leads to stroke or blackout episodes.
The procedure involves temporarily inserting a wire and over the wire a tiny balloon is passed into the narrowed segment. The ballon is inflated by a device from outside to widen the clogged artery. The balloon is then removed and a small metal tube called stent is placed and inflated to keep the dilated segment patent.
Leaking Aorta Repaired by Stenting
No, It can usually be safely implanted under local anesthesia.
At our centre we allow patients to walk the next day and the patient goes home on day 3. Generally no restriction of activities is required after day 3.
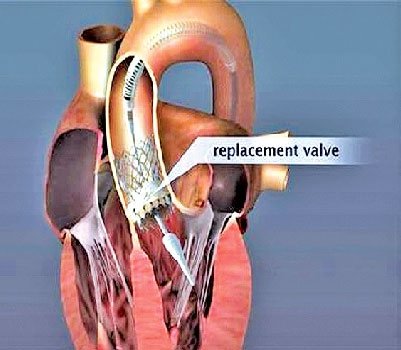
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is a procedure that allows an aortic valve to be implanted using a long narrow tube called a catheter through a large blood vessel in your groin.
TAVI is needed in patients of severe narrowing of aortic valve which is known as severe aortic stenosis . Generally these patients undergo an open heart procedure called aortic valve replacement (AVR), but in those who are too sick to undergo this major procedure TAVI is indicated as it has less risk than a conventional open heart surgery.
Your doctor will perform the procedure at a hospital. Depending on your health, they will determine what type of anaesthesia is best for you. You may be fully asleep, or you may be awake but given medication to help you relax and block pain. Your heart will continue to beat during the procedure.
A catheter is passed through the groin and the procedure is performed through this catheter. In the end a valve is implanted through this catheter that replaces the original aortic valve.
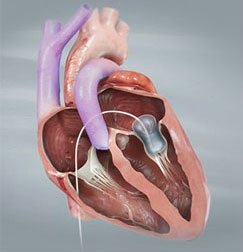
A balloon valvotomy is the a minimally invasive treatment for mitral valve stenosis. It is a procedure that widens the mitral valve so that blood flows more easily through the heart and patient is relieved of symptoms. The improved blood flow relieves symptoms. Blood pressure inside the left atrium decreases, which also helps relieve symptoms of lung congestion.
About 90 to 95 out of 100 people who are treated with a balloon valvotomy have successful outcomes and almost immediate symptom relief.
Doctors and hospitals that have a lot of experience doing balloon valvotomies tend to have higher success rates.
Balloon valvotomy is catheter-based, not surgical, and has a lower risk of complications and death than an open-heart surgery such as a commissurotomy or valve replacement.
After 3 to 7 years, about 35 to 50 out of 100 people need another procedure or surgery.
Risks during the procedure aren’t common. Complications such as blood clots or tears in the heart happen in about 1 person out of 100. Death from the procedure might happen in 1 or 2 people out of 100. Doctors and hospitals that have a lot of experience doing balloon valvotomies tend to have lower complication rates.
Complications that happen after a valvotomy include:
Mitral Regurgitation : This might happen in 2 to 10 people out of 100.1 The valve might be damaged so that it doesn’t close normally and allows blood to leak backward in the heart.
Restenosis. The valve can become narrow again after 10 to 20 years. You may require valve replacement surgery.
If your valve has narrowed again, treatment will depend on the condition of the valve. You might have another balloon valvotomy, or you might have valve replacement surgery.
Copyright © 2024 drarifwahab.com, All rights reserved